Grading System
All EBMAC programs apply a student-centered approach based on the learning outcomes and the determined assessment methods.
All units are graded on a scale of 0% to 100% (0-100 marks) which is described in the following marks and grades:
| Grade | Marks |
|---|---|
| A+ | 95% – 100% |
| A | 80% – 94% |
| B+ | 75% – 79% |
| B | 70% – 74% |
| C+ | 65% – 69% |
| C | 55% – 64% |
| D+ | 50% – 54% |
| D | 45% – 49% |
| F | 0%-44% |
The following table shows the average marks and their classification of the bachelor’s and master’s degrees:
| Classification | Marks |
|---|---|
| Pass with Distinction | 80 – 100% |
| Pass with Merit | 70 – 79% |
| Pass | 50 – 69% |
| Fail | 0 – 49% |
European Credit Transfer and AccumulationSystem

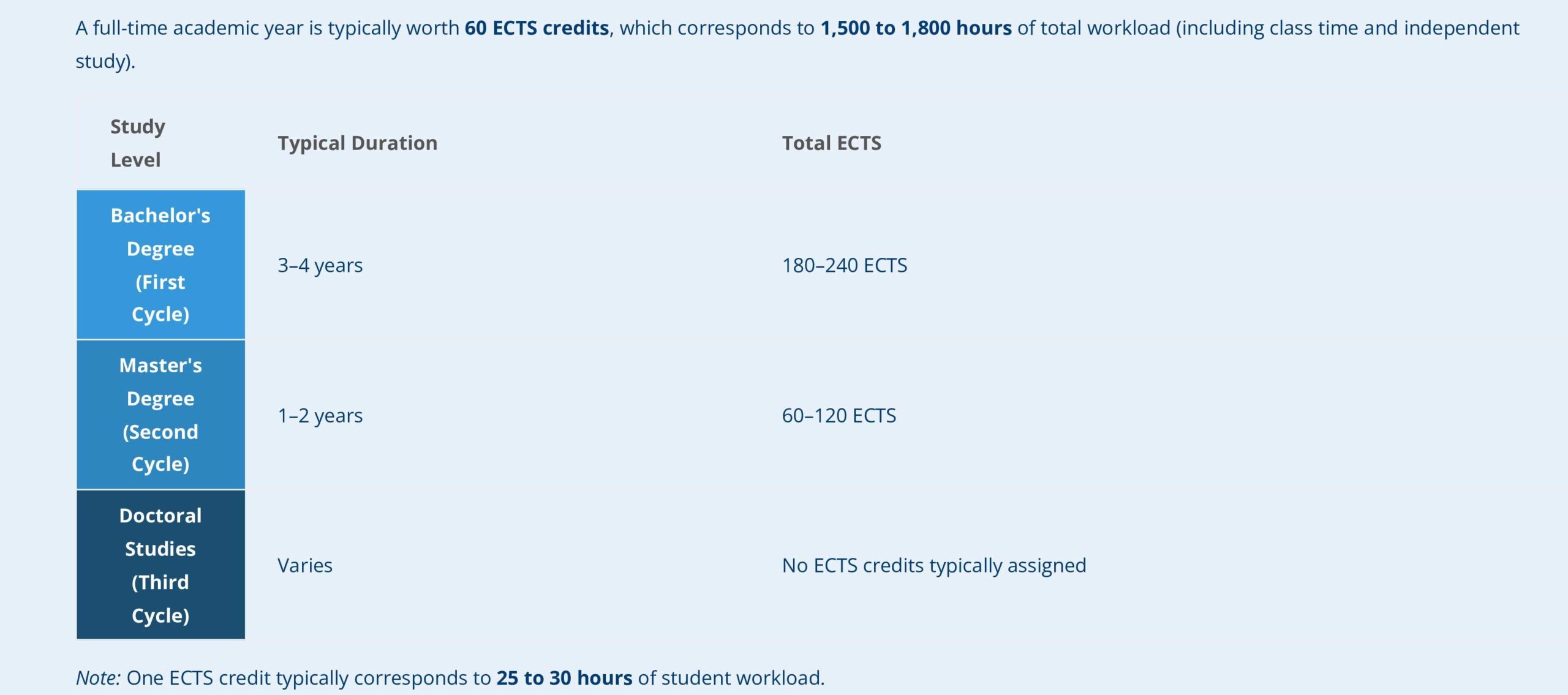
How ECTS Works?
Credit Allocation: ECTS credits are based on the total workload required to achieve specific learning outcomes. Typically, 1 ECTS credit corresponds to 25 to 30 hours of student effort, including lectures, independent study, and assessments. A full academic year usually consists of 60 ECTS credits, which equates to approximately 1500 to 1800 hours of study.
Degree Requirements: Different degrees require different amounts of ECTS credits. For example:
A Bachelor’s degree typically requires 180 to 240 ECTS credits (3 to 4 years of full-time study).
A Master’s degree usually requires 60 to 120 ECTS credits(1 to 2 years of full-time study).
How does ECTS help Students?
Recognition: ECTS improves the recognition of Academic Qualifications and Periods of Study Abroad.
Facilitates Mobility: ECTS supports student mobility by allowing credits earned in one country to be recognized in another, making it easier for students to study abroad.
Enhances Transparency: The system provides a clear framework for understanding the workload and learning outcomes associated with different courses, which helps students and institutions compare programs more effectively.


